Butcher Group 2026
In front of Scott Family Hall
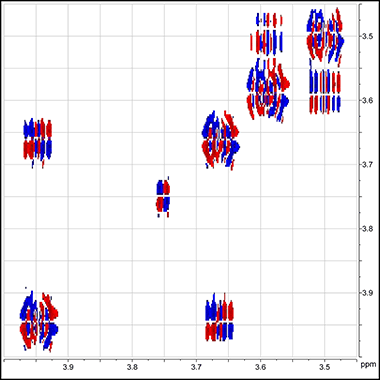
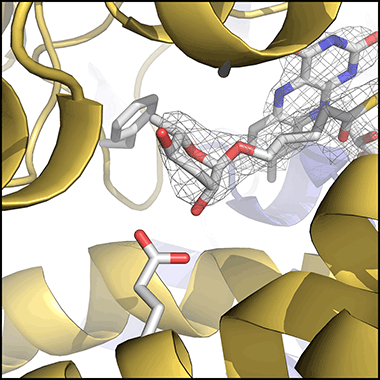
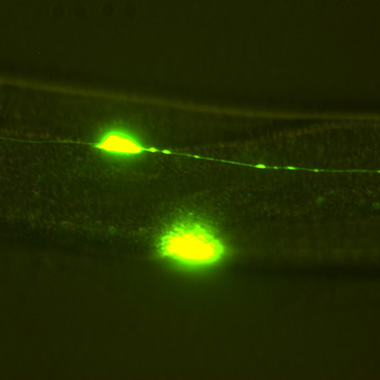
Discovering novel nematode natural products and exploring their role in chemical communication
Our lab discovers new natural products that target fundamental biological processes such as development, metabolism, and aging.